
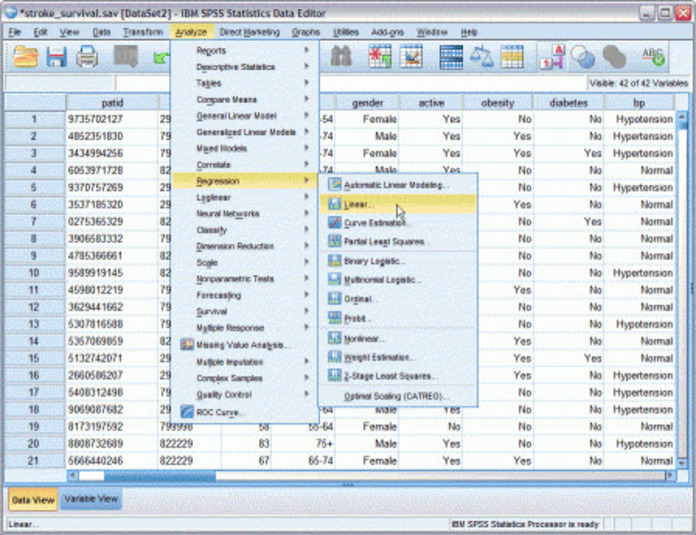
PCA is most commonly used when many of the variables are highly correlated with each other and it is desirable to reduce their number to an independent set.
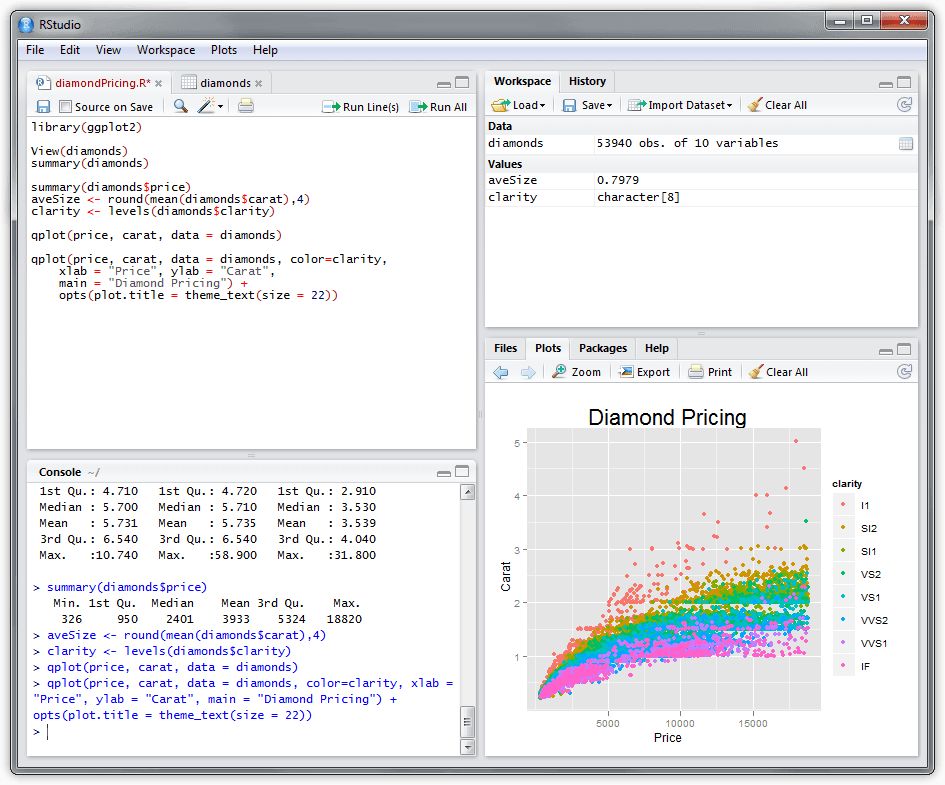

The second principal component explains the most variance in what is left once the effect of the first component is removed, and we may proceed through p p iterations until all the variance is explained. In data analysis, the first principal component of a set of p p variables, presumed to be jointly normally distributed, is the derived variable formed as a linear combination of the original variables that explains the most variance.

Principal component analysis is the process of computing the principal components and using them to perform a change of basis on the data, sometimes using only the first few principal components and ignoring the rest. These directions constitute an orthonormal basis in which different individual dimensions of the data are linearly uncorrelated. Here, a best-fitting line is defined as one that minimizes the average squared perpendicular distance from the points to the line. The principal components of a collection of points in a real coordinate space are a sequence of p p unit vectors, where the i i -th vector is the direction of a line that best fits the data while being orthogonal to the first i − 1 i-1 vectors. The vectors shown are the eigenvectors of the covariance matrix scaled by the square root of the corresponding eigenvalue, and shifted so their tails are at the mean. PCA of a multivariate Gaussian distribution centered at (1,3) with a standard deviation of 3 in roughly the (0.866, 0.5) direction and of 1 in the orthogonal direction. Principal component analysis has applications in many fields such as population genetics, microbiome studies, and atmospheric science. Many studies use the first two principal components in order to plot the data in two dimensions and to visually identify clusters of closely related data points. This is accomplished by linearly transforming the data into a new coordinate system where (most of) the variation in the data can be described with fewer dimensions than the initial data. Formally, PCA is a statistical technique for reducing the dimensionality of a dataset. Principal component analysis ( PCA) is a popular technique for analyzing large datasets containing a high number of dimensions/features per observation, increasing the interpretability of data while preserving the maximum amount of information, and enabling the visualization of multidimensional data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
